JUnit¶
单元测试¶
什么是单元测试?
- 单元测试是针对最小功能单元编写测试代码
- Java 程序的最小功能单元是方法
- 因此,单元测试就是针对单个 Java 方法的测试
JUnit 是 java 编程语言理想的单元测试框架。
JUnit 的设计¶
- TestCase:表示一个测试
- TestSuite:表示一组 TestCase,即一组测试
- TestFixture:表示一个测试环境
- TestResult:用于收集测试结果
- TestRunner:用于运行测试
- TestListener:用于监听测试过程,收集测试数据
- Assert:用于断言测试结果是否正确
注解¶
Table 1. Annotations
| JUnit 4 / JUnit 5 | Description |
|---|---|
| @Test | Identifies a method as a test method. |
| @Test(timeout=100) | Fails if the method takes longer than 100 milliseconds. |
| @Test (expected = Exception.class) | Fails if the method does not throw the named exception. |
| @Ignore or @Ignore("Why disabled") | Marks that the test should be disabled.This is useful when the underlying code has been changed and the test case has not yet been adapted.Or if the execution time of this test is too long to be included. It is best practice to provide the optional description, why the test is disabled. |
| @AfterClass / @AfterAll | Executed once, after all tests have been finished. It is used to perform clean-up activities, for example, to disconnect from a database. Methods annotated with this annotation need to be defined as static to work with JUnit. |
| @BeforeClass / @BeforeAll | Executed once, before the start of all tests. It is used to perform time intensive activities, for example, to connect to a database. Methods marked with this annotation need to be defined as static to work with JUnit. |
| @After / @AfterEach | Executed after each test. It is used to cleanup the test environment (e.g., delete temporary data, restore defaults). It can also save memory by cleaning up expensive memory structures. |
| @Before / @BeforeEach | Executed before each test. It is used to prepare the test environment (e.g., read input data, initialize the class). |
JUnit 执行逻辑:
invokeBeforeClass(StudentTest.class); // @BeforeClass
for (Method testMethod : findTestMethods(StudentTest.class)){
StudentTest test = new StudentTest();
test.setUp(); //@Before
testMethod.invoke(test); //@Test
test.tearDown(); //@After
}
invokeAfterClass(StudentTest.class); // @AfterClass
断言¶
JUnit 通过 Assert 类提供静态方法来测试某些条件。这些断言语句通常以 assert 开头。
它们允许您指定错误消息、预期结果和实际结果。断言方法将测试返回的实际值与预期值进行比较。
Table 2. Methods to assert test results
| Statement | Description |
|---|---|
| fail([message]) | Let the method fail. Might be used to check that a certain part of the code is not reached or to have a failing test before the test code is implemented. The message parameter is optional. |
| assertTrue([message,] boolean condition) | Checks that the boolean condition is true. |
| assertNotSame([message,] expected, actual) | Checks that both variables refer to different objects. |
| assertSame([message,] expected, actual) | Checks that both variables refer to the same object. |
| assertNotNull([message,] object) | Checks that the object is not null. |
| assertNull([message,] object) | Checks that the object is null. |
| assertEquals([message,] expected, actual, tolerance) | Test that float or double values match. The tolerance is the number of decimals which must be the same. |
| assertEquals([message,] expected, actual) | Tests that two values are the same. Note: for arrays the reference is checked not the content of the arrays. |
| assertFalse([message,] boolean condition) | Checks that the boolean condition is false. |
实践¶
Maven¶
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
IDEA¶
进入需要生成测试类的文件,点击文件任意处,按下快捷键:
command Ncontrol return
选择 generate Test... ,进入如下界面:
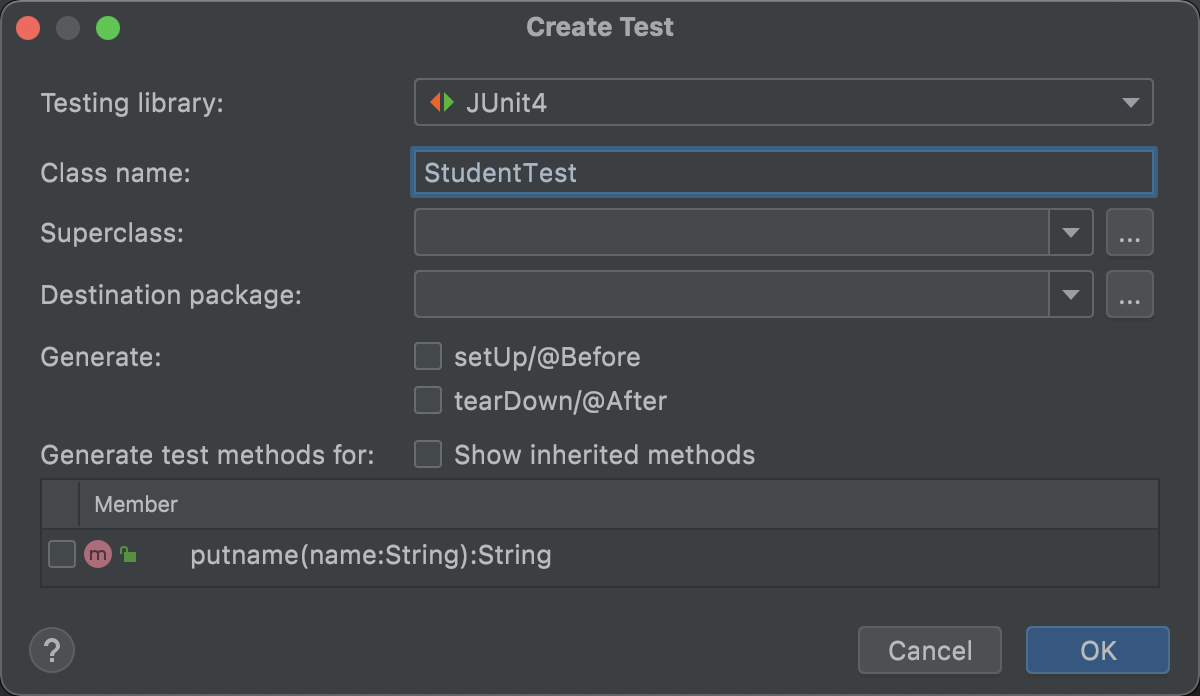
选择需要测试的方法,会自动在 /src/test/java 目录下生成测试类。
如果选择 setUp 和 tearDown ,会自动生成两个方法,注解详情看上方。
VSCode¶
文件内,右键 → 源代码操作
可以自定义快捷键,设置为:control return